Introduction
The device will be the portable computer you wish you had in the 80s. Complete with on-device programming environment, a high resolution 60Hz screen and a full QWERTY keyboard this device is all the computing power you will need on a hand held hackable device!
The connectivity of this device is unparalleled, since the SHA badge WIFI and Bluetooth connectivity have been the norm, this badge adds long range low speed connectivity (LoRa) allowing for long range mesh networking! Who doesn’t want to talk to chat with friends over a kilometer away, no infrastructure needed!
Did we mention the dual core 400MHz Risc-V ESP32-P4 CPU?
Tanmatsu or Konsool?
The open-source badge design is released under the CERN-OHL-P license. This applies to both Konsool and Tanmatsu, which are essentially the same device.
- Konsool is an open design, freely available for anyone to modify, extend, and use as they see fit.
- Tanmatsu is the pre-assembled version sold by Nicolai Electronics, eliminating the hassle of sourcing components and manufacturing the PCB.
Selling electronic devices involves additional requirements, such as safety and environmental certifications. Badge.Team appreciates that Nicolai Electronics takes on these responsibilities, offering the badge practically at cost.
By providing both an open design and ready-to-use devices, we aim to foster a thriving ecosystem, ensuring ongoing support and updates for the community.
The Konsool hardware
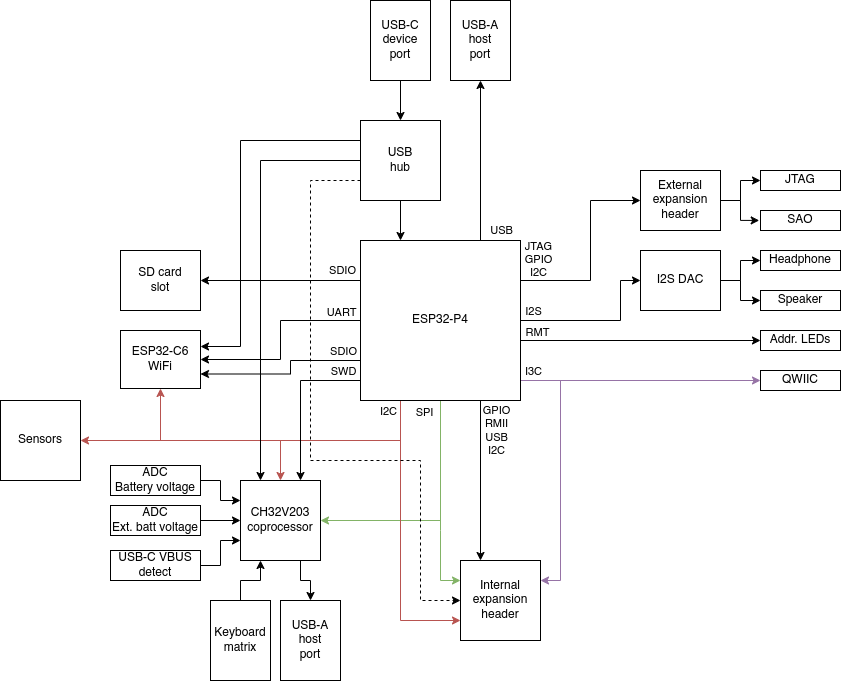
The Konsool is powered by the ESP32-P4 which is a high-performance system-on-chip (SoC) from Espressif, featuring a dual-core RISC-V CPU running up to 400 MHz with AI instruction extensions. It integrates high-speed peripherals, including USB OTG 2.0 HS and Ethernet. The ESP32-P4 is tailored for applications requiring rich human-machine interfaces and power efficient computing. Making it (in our humble opinion) a good choice for a battery held device that humans interact with.
Additionally, an ESP32-C6 module provides WiFi, Bluetooth Low Energy, and IEEE802.15.4 wireless connectivity. This allows for internet access as well as compatibility with local mesh networks like Thread and ZigBee, ideal for developers and enthusiasts.
A LoRa radio module enables communication over LoRa networks, including long-range mesh services and classic (G)FSK modulation at either 433, 868 or 915MHz, depending on the module installed.
The device includes 16MB of built-in flash storage for firmware and applications, expandable via a micro SD card slot. This slot supports SD cards at both standard and high-speed (SDIO 3.0).
User interaction is provided through a QWERTY keyboard and a MIPI DSI display.
The expansion port enhance Konsool’s versatility by supporting expansion an board on the back of the the device. Exposing SPI, I2C, USB (2.0) and GPIO to the expansion board provides ample connectivity options for expansion board designs.
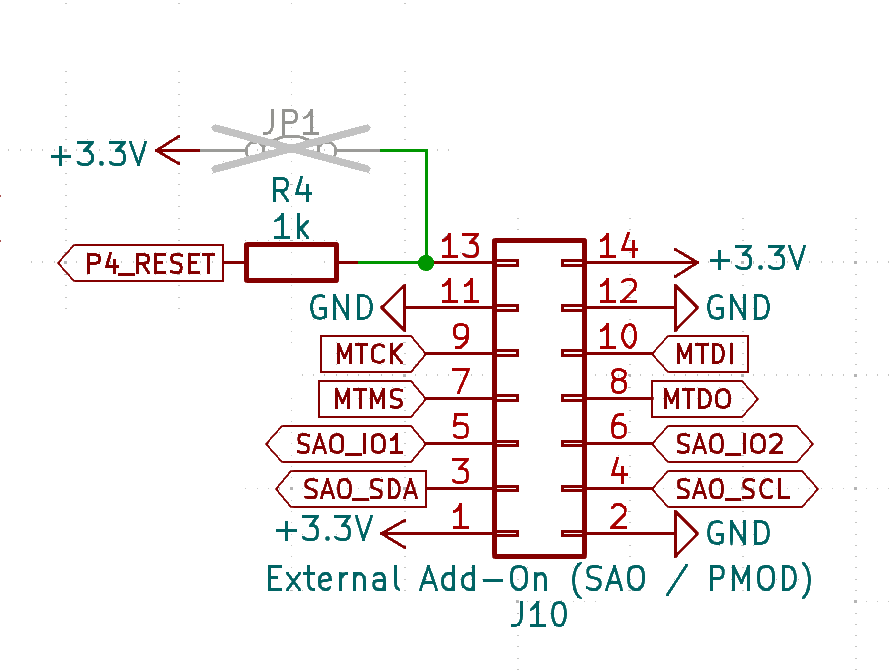
The side-facing CATT port provides connectivity to a JTAG debugger, and various PMOD and SAO-compatible accessories.
A QWIIC compatible connector allows the device to interface with numerous sensors from manufacturers like Sparkfun and Adafruit.
The ESP32-P4 also includes hardware-accelerated encoding of h264 video through its MIPI DSI and CSI interfaces. This powerful CPU can record video from devices such as a Raspberry Pi camera, encode it, and stream it wirelessly over WiFi.
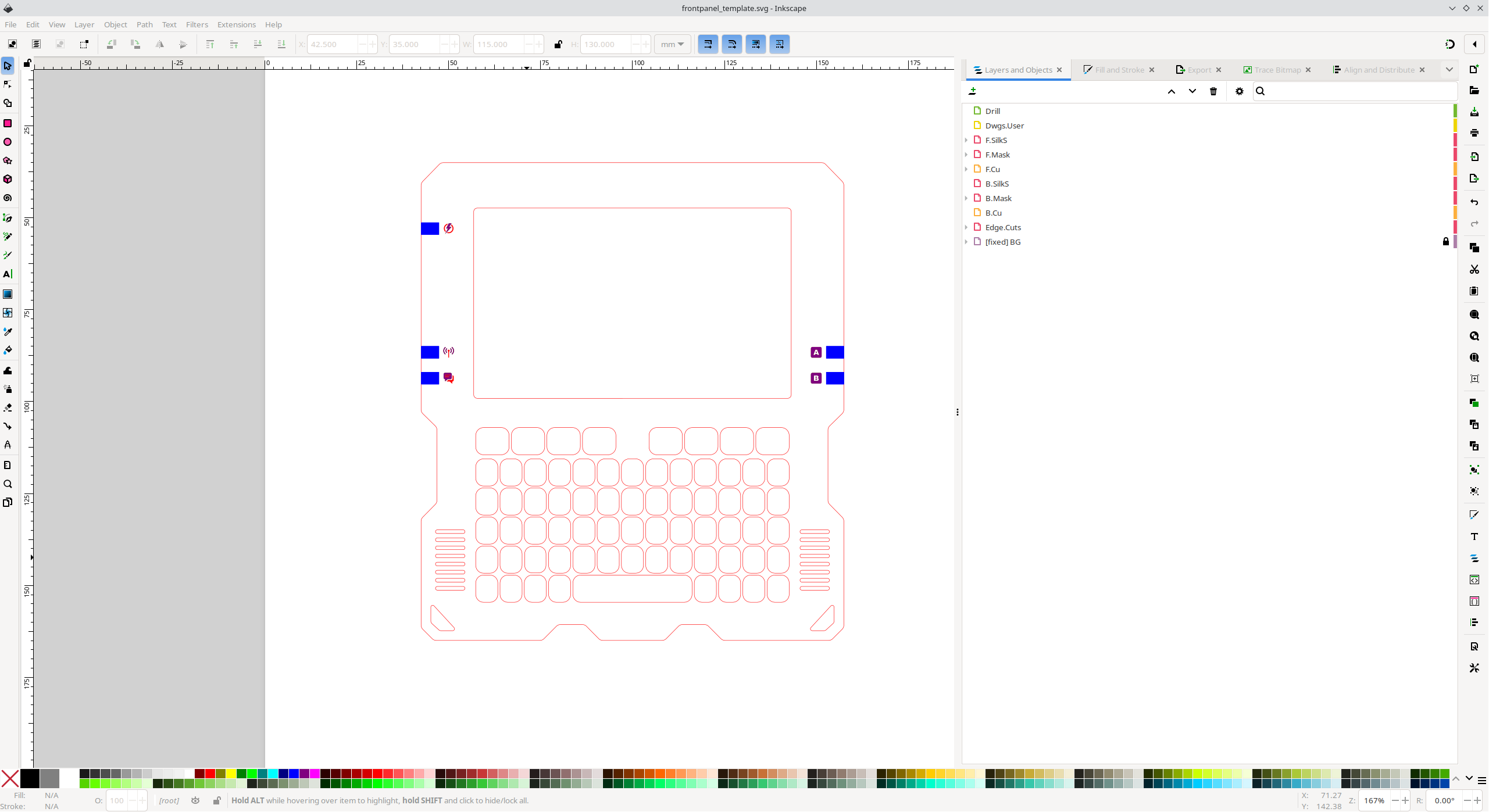
Custom front panels are feasible using the provided information, and 3D printable case designs are also available for those interested in additional customization. (A Case design in FreeCAD format coming soon)
The team
The Konsool would not have been possible without the help of our amazing volunteers.
| Nick | Name | Role |
|---|---|---|
| r3nz3 | Renze Nicolai | Hardware and Software development |
| Ranzbak | Paul Honig | Hardware, Testing and Documentation |
| Jhaand | Jelle Haandrikman | Testing and review |
| RobotMan2412 | Julian Scheffers | Software and Testing |
| Ankhaneko | Nikolett | Artwork and more |
| Orange Murker | Luna | Software and Testing |
| NightOwlNL | Emiel Bart | Documentation |
| Noor | Testing | |
| Jay | Jay Visschedijk | Ergonomic board outline |
| Wietsman | Wietse Boonstra | Component footprints |
| Kliment | Kliment Yanev | Review hardware |
| Anus | Anne Jan Brouwer | Software |